SPI Screen Parameter Configuration¶
Interface Description¶
In software, SPI interfaces are first categorized into two major types based on whether there is a physical D/CX line: LCDC_INTF_SPI_DCX_xxx and LCDC_INTF_SPI_NODCX_xxx. Then, they are further classified based on the number of data lines used during bulk data transfer (i.e., 0x2C/0x3C commands), which can be 1~4DATA. Finally, additional labels such as DDR and AUX are added based on whether DDR mode is used and whether PTC assistance is required.
Generally, 3-line SPI refers to interfaces without a physical D/CX line, while 4-line SPI has a physical D/CX line.
The D/CX line pinmux is usually LCDC_SPI_DIO1.
SPI interface command read and write operations are always in single-line mode, but during bulk data transfer (0x2C/0x3C commands), data can be transferred in parallel using 1~4 lines.
Interface Name |
Physical D/CX Line |
Parallel Data Lines for 0x2C/0x3C Bulk Data Transfer |
Other |
|---|---|---|---|
LCDC_INTF_SPI_DCX_1DATA |
Yes |
1 |
- |
LCDC_INTF_SPI_DCX_2DATA |
Yes |
2 |
- |
LCDC_INTF_SPI_DCX_4DATA |
Yes |
4 |
- |
LCDC_INTF_SPI_DCX_4DATA_AUX |
Yes |
4 |
Ramless screen |
LCDC_INTF_SPI_DCX_DDR_4DATA |
Yes |
4 |
DDR mode |
LCDC_INTF_SPI_NODCX_1DATA |
No |
1 |
- |
LCDC_INTF_SPI_NODCX_2DATA |
No |
1 |
- |
LCDC_INTF_SPI_NODCX_4DATA |
No |
1 |
- |
Screen Parameter Configuration Explanation¶
4-line/3-line SPI Interface¶
static LCDC_InitTypeDef lcdc_int_cfg =
{
/*
3-line SPI mode, 2 data lines for bulk data transfer
*/
.lcd_itf = LCDC_INTF_SPI_NODCX_2DATA,
/* QSPI clock frequency selection, the frequency is the result of dividing the hcpu main frequency, for example, if the hcpu main frequency is 240MHz, the available frequencies are 40/48/60/80. If 62MHz is set, it will actually be set to 60MHz */
.freq = 24000000,
.color_mode = LCDC_PIXEL_FORMAT_RGB565,
.cfg = {
.spi = {
.dummy_clock = 0, /* In QSPI read mode, the number of empty clock cycles between cmd and data, default is 0, no need to modify */
/* This option is to avoid image tearing (cause of tearing: when the screen reads RAM data, QSPI is also writing data to RAM) */
#ifdef LCD_ST7789P3_VSYNC_ENABLE
.syn_mode = HAL_LCDC_SYNC_VER,/* Enable checking the TE signal from the screen and synchronize data writing to RAM. Enabling this configuration will cause a system hang if the screen does not output a TE signal */
#else
.syn_mode = HAL_LCDC_SYNC_DISABLE,/* Disable checking the TE signal from the screen. Use this configuration when debugging the screen driver and not considering tearing issues */
#endif
/*
This configuration is meaningful only when HAL_LCDC_SYNC_VER is selected. It is used to configure the polarity of the TE (Vsync) signal.
Set to 1 if TE is normally low and high when data can be written to RAM
*/
.vsyn_polarity = 0,
.vsyn_delay_us = 1000,/* This configuration is meaningful only when HAL_LCDC_SYNC_VER is selected. It is used to configure the delay in microseconds after the TE signal goes high before data is written to RAM */
.hsyn_num = 0,/* This configuration is meaningful only when .syn_mode is set to HAL_LCDC_SYNC_VERHOR. It is used to configure the number of clock pulses after the TE signal goes high before data is written to RAM */
/*
1. During QSPI read operations, CMD is always output from D0, but the read data can be output from D0-D3 depending on the screen driver IC. This configuration is for compatibility with different screen driver ICs.
2. Can be set to 0-3. Refer to the screen driver IC datasheet to select the appropriate QSPI read signal from D0 - D3
*/
.readback_from_Dx = 0,
},
},
};
The following is a waveform diagram for 4-line TE not enabled, showing that the TE waveform is not aligned with the SPI CS falling edge.
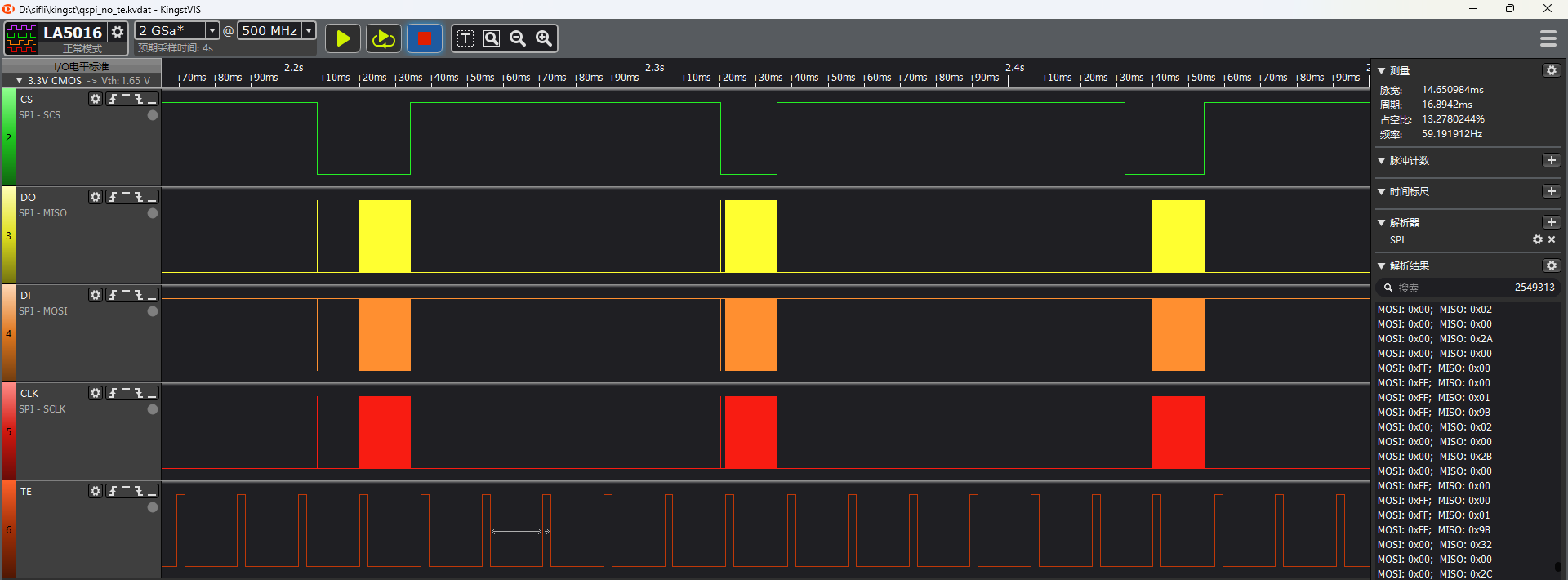
Frame Rate Testing Method¶
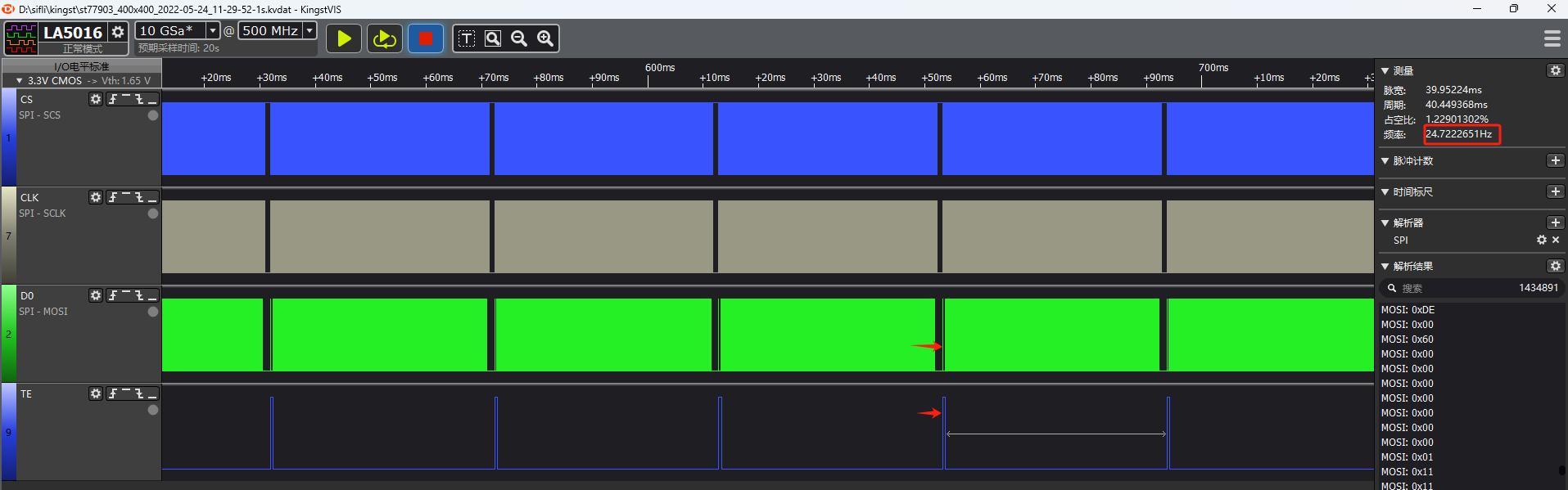
Enable the HAL_LCDC_SYNC_VER configuration. The SPI timing is as shown in the following diagram, where the screen update is synchronized with TE.
In a UI with a very high frame rate, measure the frequency of the TE signal, which represents the screen refresh rate.
QSPI Interface¶
#ifdef LCDC_USE_DDR_QSPI
#define QAD_SPI_ITF LCDC_INTF_SPI_DCX_DDR_4DATA
#define QAD_SPI_ITF_FREQ 40000000
#else
#define QAD_SPI_ITF LCDC_INTF_SPI_DCX_4DATA
#define QAD_SPI_ITF_FREQ 48000000
#endif
static LCDC_InitTypeDef lcdc_int_cfg_spi =
{
/*
1. DDR (qspi's clk double-edge data transfer mode) select LCDC_INTF_SPI_DCX_DDR_4DATA
2. SDR (qspi's clk single-edge data transfer mode) select LCDC_INTF_SPI_DCX_4DATA
*/
.lcd_itf = QAD_SPI_ITF, //LCDC_INTF_SPI_NODCX_1DATA,
/*
1. QSPI's clk frequency selection, the frequency is the frequency after dividing the hcpu main frequency, for example, if the hcpu main frequency is 240MHz, the available frequencies can only be 40/48/60/80. If 62MHz is set, it will actually be set to 60MHz.
2. The QSPI's clk frequency should not be set too high in DDR mode.
*/
.freq = QAD_SPI_ITF_FREQ,
/*
1. LCDC_PIXEL_FORMAT_RGB565 is the common RGB565 color format.
2. LCDC_PIXEL_FORMAT_RGB888 is the common RGB888 color format.
*/
#if LV_COLOR_DEPTH == 24
.color_mode = LCDC_PIXEL_FORMAT_RGB888,
#else
.color_mode = LCDC_PIXEL_FORMAT_RGB565,
#endif
.cfg = {
.spi = {
.dummy_clock = 0, /* In QSPI read mode, configure the number of empty clk cycles between cmd and data, default is 0, no need to modify */
/* This option is to avoid image tearing (cause of tearing: when the screen reads RAM data, QSPI is also writing data to RAM) */
#ifdef LCD_FT2308_VSYNC_ENABLE
.syn_mode = HAL_LCDC_SYNC_VER, /* Enable checking the TE signal sent by the screen and synchronize data writing to RAM. Enabling this configuration, if the screen does not output a TE signal, it will result in inability to write data to RAM, causing a system hang. */
#else
.syn_mode = HAL_LCDC_SYNC_DISABLE, /* Disable checking the TE signal sent by the screen. This configuration is used during initial screen driver debugging when tearing is not a concern. */
#endif
/* This configuration is meaningful only when HAL_LCDC_SYNC_VER is selected, used to configure the polarity of the TE (Vsync) signal */
.vsyn_polarity = 1, /* Configure 1, TE is normally low, and data can be written to RAM when TE is high */
.vsyn_delay_us = 0, /* This configuration is meaningful only when HAL_LCDC_SYNC_VER is selected, used to configure the delay in us after the TE signal goes high before writing data to RAM */
.hsyn_num = 0, /* This configuration is meaningful only when .syn_mode is set to HAL_LCDC_SYNC_VERHOR, used to configure the number of clk pulses after the TE signal goes high before writing data to RAM */
/*
1. During QSPI data read, CMD is always output from D0, but the read-back data, depending on the screen driver IC, can be output from D0-D3. This configuration is for compatibility with different screen driver ICs.
2. Can be configured from 0-3, refer to the screen driver IC's datasheet to select the corresponding QSPI read signal from D0 - D3.
*/
.readback_from_Dx= 3, /*!< 0 read back data from D0 (HW SPI support), 1 read back from D1 (Software SPI support).*/
#ifdef LCDC_USE_DDR_QSPI
.flags = SPI_LCD_FLAG_DDR_DUMMY_CLOCK,/* This flag is for adapting to DDR screens, adding a few empty clocks after sending the framebuffer in DDR mode. */
#endif /* LCDC_USE_DDR_QSPI */
},
},
};